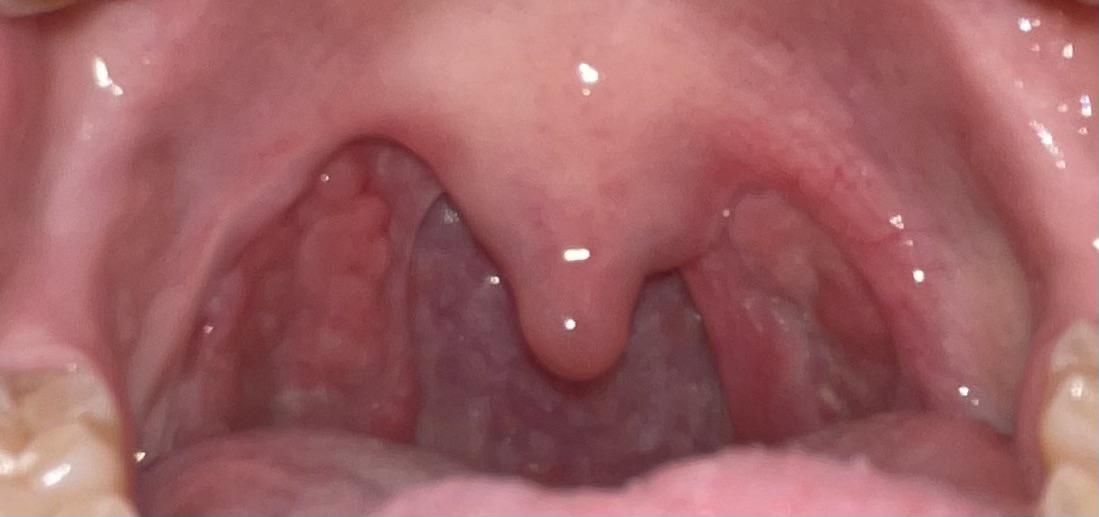
Understanding Tonsillectomy
A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the complete removal of the tonsils, which are two lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who experience recurrent tonsillitis, obstructive sleep apnea, or other related ailments that affect their quality of life. In some cases, large tonsils can interfere with breathing, swallowing, or even speaking, leading to the need for surgical intervention.
can tonsils grow back after being removed? – tymoff
Before undergoing a tonsillectomy, patients often experience various symptoms, including sore throats, difficulty swallowing, and recurrent fevers. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, prompting consultations with healthcare providers. The decision to proceed with a tonsillectomy is usually made collectively with the patient, their family, and the doctor after evaluating the frequency of tonsillitis episodes, complications, and responses to other treatments.
The surgical process generally takes less than an hour, and it can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s specific situation and the surgeon’s recommendations. After the removal of the tonsils, patients are usually monitored for a few hours before being discharged. The recovery period can vary from person to person, but most individuals can expect to feel discomfort for several days, which can often be managed with pain medication. Adequate hydration and a soft diet are also advised during recovery.
Many people wonder whether can tonsils grow back after being removed, as the tonsils serve some immune function. However, it’s essential to understand that the surgical removal of tonsils is generally permanent. Patients may notice changes in their overall health and immune response post-surgery, warranting discussions with their healthcare provider to address any concerns relating to the potential for regrowth or the body’s ability to adapt.
Can Tonsils Regrow? The Science Behind It
The idea that tonsils can regrow after surgical removal has intrigued both patients and medical professionals alike. While the common understanding is that tonsillectomy, the procedure for removing the tonsils, is permanent, there are instances in which individuals have reported regrowth. This phenomenon is primarily attributed to several anatomical and physiological considerations. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system and comprise lymphoid tissue that plays a crucial role in immune response. When tonsils are partially removed rather than entirely excised, remnants of the lymphoid tissue may thrive and develop, resulting in the perception of regrowth.
Medical literature indicates that cases of regrowth are not widely prevalent but are acknowledged within clinical observations. Studies reveal that the presence of residual tonsillar tissue post-surgery can lead to a reemergence of tonsil-like structures, particularly if the excised tissue did not encompass the entire tonsil. Also, the body’s natural capacity for tissue regeneration can facilitate this process. Some research points to variations in surgical techniques, where complete removal is not achieved, hence contributing to the potential for regeneration.
Experts emphasize that while it is possible for tonsils to regrow, the conditions under which this occurs are often specific and not necessarily indicative of a failure in the original surgery. Given the complexities of the lymphatic system and individual anatomical differences, regrowth can also depend on factors such as age, overall health, and immune function. Understanding these nuances is crucial for patients considering tonsillectomy and managing their expectations regarding future health concerns. Ultimately, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals for personalized insights into the likelihood of tonsil regrowth, especially in the case of recurrent throat infections or sleep apnea.
Symptoms and Risks of Regrown Tonsils
The regrowth of tonsils, while uncommon, is a concern for individuals who have undergone a tonsillectomy. It can manifest with a variety of symptoms that resemble the issues leading to the initial surgery. Individuals may experience sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen glands in the neck. These symptoms could indicate that tonsils are regrowing or that there might be an underlying health issue. Those who had chronic infections prior to their surgery should be particularly vigilant for these signs, as regrown tonsils can lead to similar complications.
In addition to the above symptoms, frequent bad breath, persistent throat discomfort, or changes in voice can also suggest that tonsils may be returning. It’s crucial to understand that these symptoms can sometimes mimic other conditions, making it imperative for individuals to seek medical evaluation if they notice any changes in their throat health post-surgery. Regular check-ups can help monitor for the potential regrowth of tonsils, ensuring timely medical intervention if necessary.

The risks associated with regrown tonsils include recurrent infections, chronic inflammation, and even the eradication of the benefits gained from the initial surgery, such as reduced frequency of throat infections. For some, these risks can severely impact their quality of life, leading to missed school or work days. In severe cases, regrown tonsils may obstruct breathing, especially during sleep, potentially leading to obstructive sleep apnea—an important consideration for parents monitoring their children’s health post-tonsillectomy.
Given these considerations, it is essential for patients to be proactive in monitoring their throat health even after a tonsillectomy. Remaining aware of changes and consulting a healthcare professional if symptoms arise can help prevent further complications and ensure appropriate management of throat conditions.
Preventive Measures and Future Considerations
Following a tonsillectomy, it is essential to adopt preventive measures that may help minimize the likelihood of tonsils growing back after being removed. Regular monitoring of one’s health, particularly oral and throat health, plays a crucial role in achieving this aim. Patients should maintain consistent communication with healthcare providers to discuss any concerning symptoms or complications post-surgery.
One significant lifestyle modification involves enhancing daily health practices. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health and boost the immune system, which may help in the prevention of throat infections that could lead to further complications. Additionally, incorporating adequate hydration and proper oral hygiene practices into daily routines will contribute to throat health. Avoiding irritants such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can reduce the risk of inflammation and infections.
Regular medical check-ups enable early detection of any potential issues related to the throat or other connected systems in the body. Through ongoing assessments, healthcare providers can offer tailored advice and interventions. They can also discuss the individual risks related to tonsil regrowth and alternative treatment options should complications arise.
can tonsils grow back after being removed? – tymoff
Further advancements in medical research are continuously evolving in regard to tonsil health. Ongoing studies are focused on understanding the underlying causes of recurrent tonsil issues, which may lead to innovative treatments or preventive approaches in the future. For patients who have undergone tonsillectomy, staying informed about these developments can provide peace of mind and alternative solutions should symptoms recur.
In conclusion, maintaining a proactive approach to health through lifestyle changes, regular medical evaluations, and awareness of ongoing research can significantly reduce complications related to tonsils after surgery. This comprehensive strategy is pivotal for those seeking to safeguard against issues and improve their overall wellness.
May Be You Also Read

